Project management has become essential in today’s competitive environment. What is project management? How important does it need to be?
Despite statistical evidence showing that a mature, well-defined process for managing projects makes companies far more likely to deliver their promises on time and under budget, only 46% of organizations make this a cultural value.
Maybe you've always wanted to grow your business operations, or perhaps you already manage someone else's project. It's important to get good at managing projects because they come in all shapes and sizes. Whether you're working with clients, freelancers, colleagues, or family members, knowing how to properly run a project will help you accomplish more, and enjoy it too.
Project management encompasses the entire project lifecycle from concept through completion. If your company has multiple projects going on simultaneously, then project management is even more critical. The manager will oversee the activities of each team member, monitor their performance against standards, and provide feedback on things such as timeliness and quality.
Being able to successfully plan and execute a project comes down to four basic skills: prioritization, communication, collaboration, and leadership. When these four skills are mastered, you'll achieve success across every aspect of your life. This course will teach you how to apply those skills to projects, whether it's your job or personal endeavours.
|
What is Project Management? Project management is defined as the framework used to guide your team to success—this includes your team objectives, tools, and techniques both over the long term and in your day-to-day work. |
What Is Project Management?
Project management involves the planning and organizing of a business's resources to complete a specific task, event, or responsibility. It may involve a single project or an ongoing activity involving people, finances, technologies, and intellectual properties.
Project managers are usually associated with fields in engineering, construction, and IT, which tend to have a complex set of elements that need to be completed and assembled into a working project. However, marketing agencies do a lot of project management (PM) and at times manage projects at different stages simultaneously.
Regardless of the type of business, the role of the project manager is usually to help set the goals for the projects and to manage the completion of the various parts of the projects. They also create checkpoints to ensure completed parts meet a certain standard.
Why is project management important?
Project management aims to produce an end product that will affect some kind of positive outcome for the organization that initiated the project. It is the initiation plan for a series of tasks needed to complete an end product. Projects that require formal project management are those that:
- produce something new or altered, tangible or intangible;
- has a fixed length: a clear beginning and end;
- are often complex, involving a lot of work or teams involved.
- require the ability to manage change
- require the management of risk investment in effective projects will have several advantages, including:
- increasing the chances of achieving the desired outcome.
- ensuring efficient and best value use of resources
Types of Project Management
There are many different kinds of project management tools available for use by various kinds of companies. They include the following:
1. Waterfall project management
Waterfall project management or traditional project management is based on the idea that everything must happen according to plan. You break down projects into phases, assign tasks, and build timelines to ensure delivery dates are met. This method works well for large, complex projects. But it doesn't work very well for smaller projects because it requires too much upfront planning. And it won't help you manage change effectively.
2. Agile project management
Agile project management is more flexible than waterfall project management. Instead of setting out all steps ahead of time, agile project management relies on small iterations called sprints. Each sprint has a goal and scope, which can vary depending on what stage the project is at. The key difference between agile and waterfall project management is that agile allows for constant change throughout the process. Agile project management is the approach for Growth-Driven Design projects.
3. Lean project management
Lean project management focuses on eliminating waste from processes. Waste occurs when there's no need for something, like unnecessary meetings, or if there's not enough time to complete a task, like waiting for materials to arrive. By focusing on these two areas, lean project management helps reduce costs and increase efficiency.
4. Scrum project management
The Scrum framework is one of the most popular ways to implement agile project management. This framework breaks down large projects into smaller ones, called "sprints," that are usually four weeks long. It lays out rules for team sizes, team roles, planning and meetings, deliverables, etc.
While popular among software developers, the Scrum framework is also great for teams that want to deliver working increments of their work during a project. You might use it for marketing campaigns or product design.
5. Kanban project management
Kanban project management is another form of agile project management. It's similar to scrum but with a focus on flow instead of backlogs. Kanban is used to track where your bottlenecks are and how long each step takes.
Kanban project management is based on the concept of visualizing work in progress (WIP). This method allows you to see what needs to be done next, and it gives you a clear picture of where things stand. You can easily identify bottlenecks and plan accordingly.
Unlike the Waterfall framework, which relies heavily on sequential planning, Kanban focuses on continuous improvement. Instead of having a detailed plan of exactly what must happen, Kanban uses a simple WIP board to help manage projects.
Project Management Process
The Project Management Institute (PMI) defines the project management lifecycle as having five distinct phases, including initiation, planning, executing, monitoring, and closing. While many people think of the project management lifecycle in terms of these steps, it consists of much more than just those five phases.
The PMI breaks down the entire project management lifecycle into five distinct phases that are relatively well agreed upon in the project management environment.
1. Initiation
Before embarking on a new project, it helps if you're well prepared so you don't run into unexpected challenges. During the initial planning stage for a new project, set up the following things:
Project Scope: the specific limitations and boundaries for the project. It covers what will be done in the course and what won't (i.e.project objectives).
High-level project overview: A high-level description of the resources, time, SMART goals, and requirements needed to finish a particular task. You'll be able to track these requirements throughout the project.
Budgets: How big is the budget required for a successful project?
You may establish a project charter or Project Initiation Document (PID) for larger projects.
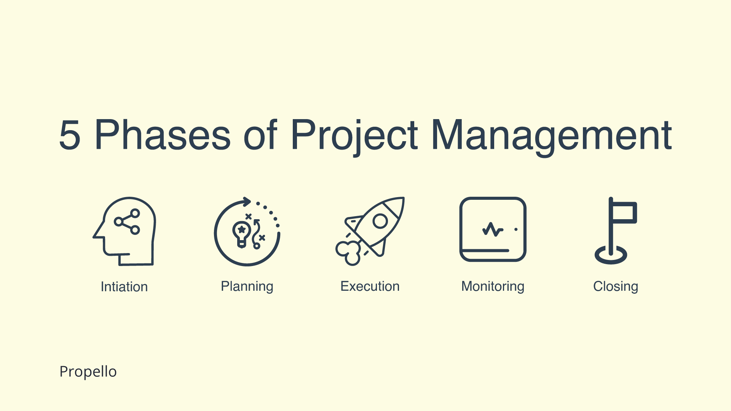
2. Planning
During this stage, key milestones and deadlines are set, which include the final project deadline. If you're clear and intentional about when you want something done, then you can get everyone involved moving towards the same goal at the same time. This will help you avoid unnecessary confusion later on when you encounter roadblocks.
It's important during this process to outline which project management methodology the teams will use. There are many different ways to organize projects into phases. Some of them include Agile, Waterfall, PRINCE2/PMI, Scrum, Lean/Toyota Production System, and Kanban.
The planning phase also includes:
- Selecting the team members
- Defining deliverables
- Resource estimation
- Determining which activities are related
3. Execution
At this point, it's "all about getting stuff done." You've completed the planning and analysis phases and are ready to execute your project plan. In addition, you'll continue to monitor progress and control the quality of the output produced during the execution phase.
During the execution phase, you'll carry out the details of the project plan to deliver your products to the appropriate stakeholders. For example, you may want to complete the following activities:
- Manage workflow tasks
- Recommend changes and corrective actions
- Communicate status and provide feedback
Execution involves managing the flow of information, resources, and activities across teams and organizations. To do that effectively, you must understand how each team member works best and what tools and techniques help them accomplish their goals.
4. Monitoring
Project management is about managing change. Change doesn't happen overnight. Most projects experience significant changes throughout execution. These changes can include scope creep, schedule slippage, resource availability issues, etc. Managing change effectively is critical to project success. Without effective change control, projects often fail.
Change is inevitable. As a result, project managers must develop methods to monitor and control change throughout the lifecycle of a project. Monitoring is the process of checking whether things are happening as planned. Controlling is the process of adjusting plans based on what is occurring.
Monitoring and controlling work together. They are both vital to successful project management. If you don't know where you are, how do you know where you're going? And if you don't know where the project is headed, how do you know how to get there? To manage change effectively, project managers must monitor and control progress throughout the project lifecycle.
Project managers need to be able to tell whether they're ahead or behind schedule at any particular time during the project lifecycle. where should we be according to the project plan? Effective monitoring requires:
Regular, consistent project “check-ins”
Proper use of project management tools and frameworks (like Kanban boards, GANTT charts, and stand-up meetings) can help teams stay organized and focused. The more visual and interactive this is, the easier it is for people to understand it and interact with it.
5. Closing
The project delivery phase is often the most important part of the process because it involves wrapping up all activities and delivering the final product to the customer. At the end of the day, the purpose of the project is to help the customer achieve his or her goals. As such, it’s critical to ensure that the project delivers value to the customer.
This is where many projects fail, simply because there isn’t enough thought put into the closing stage. You can spend hours writing a report about everything that happened during the project, but unless you follow up with the stakeholders and close the loop, it won’t do much good.
There are three main reasons why project deliveries don’t happen:
- Lack of planning
- Poor communication
- Unrealistic expectations
To avoid these problems, project managers need to make sure that they have a clear understanding of the deliverables before starting the project. This will allow them to communicate clearly with the stakeholders and set realistic expectations. It also helps them identify potential risks early in the process so that they can take steps to mitigate those risks.
Putting it all together
Project management is an ever-changing discipline that requires project managers and their teams to deliver work on time and within budget. While there are many ways to approach managing projects, one thing is certain: to succeed, every team needs a clear vision of what success looks like, along with the proper tools to help bring that vision to life. Collaboration is at the core of effective project management; without it, the entire process falls apart.
The good news is that today, we live in a world where technology makes collaboration easier than ever. With online meetings, task lists, chat rooms, and document-sharing platforms, it's easy to collaborate with anyone anywhere. And thanks to the rise of cloud computing, it's even possible to access those resources from almost any device. But despite the convenience, collaboration still takes some effort. To ensure everyone stays engaged throughout the project, you'll need to use the right tools.